
Form W-9 is used for tax purposes in the US. Although it is an IRS form, it is not submitted to the IRS. Rather, it is used for submitting a Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) and other information to a requester.
In this guide, we’ll explore the full purpose of this form, when you need to use it, and what happens if you fail to submit it. We’ll also answer the most frequently asked questions about Form W-9.
- What is Form W-9?
- When and why to use Form W-9
- The essentials of Form W-9 for taxes
- Form W-9 for businesses and individuals
- Legal and privacy considerations
- A brief overview of filling out Form W-9
- W-9 vs. Form 1099 overview
- Reporting and withholding
- FAQs
- Conclusion
What is Form W-9?
Form W-9, also called a Request for Taxpayer Identification Number and Certification form, is an IRS form that’s used for the formal request and submission of a Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) and other important information.
The most common use of Form W-9 is for tax purposes, often between a payee and a payer who has requested the form. When it is requested, the payee fills out and submits Form W-9 to the payer.
As Form W-9 requires the payee’s signature, it also serves as a certification that the submitted information is accurate and that the payee is not subject to backup withholding. This is a withholding rate of 24% on the payment owed if the payee fails to submit Form W-9 or provide a correct TIN.
When and why to use Form W-9
Form W-9 is typically requested by a business or company when it needs a TIN to file Form 1099 with the IRS. This can be for:
- Owed income
- Real estate transactions
- Mortgage interest
- Acquisition or abandonment of secured property
- Cancellation of debt
- Contributions made to an IRA
The most common reason is for owed income, such as when a business will receive and pay for services from an independent contractor or freelancer. The business will request the self-employed individual to submit Form W-9.
Once submitted, the business can then use the provided information to file Form 1099 with the IRS if the payments are $600 or more for that year. So, while Form W-9 is not filed with the IRS, it is needed for filing Form 1099.
The essentials of Form W-9 for taxes
Form W-9 plays an essential role in the request and submission of an individual’s TIN and other important information. This information can then be used for other tax purposes, including the filing of a year-end Form 1099.
Form W-9 is also important for remittance in the event of backup withholding. If a payee fails to submit Form W-9 after it is requested, the payer must remit a withholding rate of 24% to the IRS on non-employment income owed to the payee. This is to ensure that taxes are collected by the IRS on the payee’s income.
Form W-9 for businesses and individuals
Form W-9 is important for businesses and individuals, i.e. self-employed independent contractors or freelancers. Businesses must request Form W-9 to collect information from these individuals before using their services. This information includes:
- Name
- Business name or disregarded entity name
- Federal tax classification
- Exemptions
- Address
- TIN — a Social Security number (SNN) for individuals or an Employer Identification Number (EIN) for other entities
Once submitted, businesses can use the provided information to file Form 1099 and report the payment both to the IRS and to the individual who was paid.
For individuals, it’s important to submit Form W-9 when it is required to avoid backup withholding and other penalties.
Legal and privacy considerations
There are legal considerations around Form W-9 for both payers and payees.
Payers need to request Form W-9 to be able to file IRS Form 1099, which is required for reporting non-employment income of $600 or more.
It’s also important for backup withholding, as the IRS can impose penalties on payers if the payer does not resort to backup withholding when Form W-9 is not submitted by a payee.
As a result, payees need to submit Form W-9 to avoid backup withholding. This is a 24% reduction on non-employment income that is paid to the IRS by the payer. Failure to provide a correct TIN can also result in an IRS penalty of $50.
A brief overview of filling out Form W-9
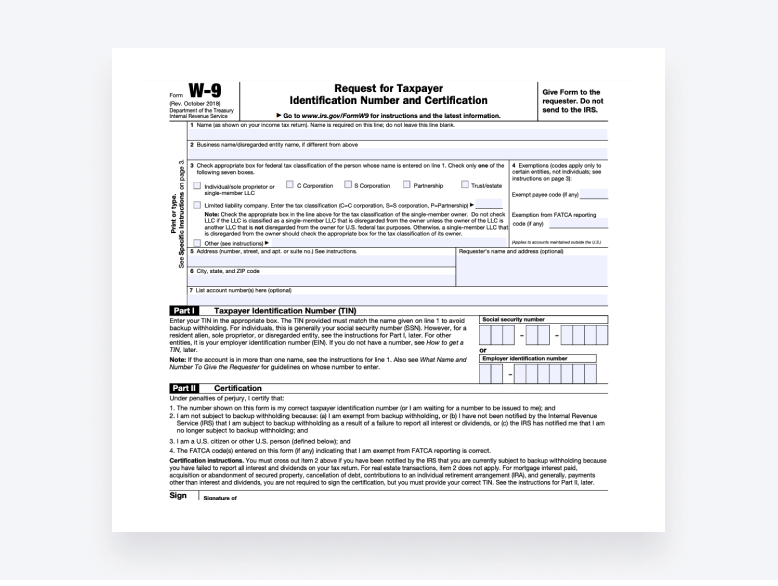
Form W-9 comprises six pages in total, but only the first page needs to be filled out. The first section is for providing:
- Name
- Business name or disregarded entity name
- Federal tax classification
- Exemptions (if applicable)
- Address
- City, state, and ZIP code
- Requester’s address (optional)
- Account numbers (optional)
Part I is for providing the TIN and Part II is for certifying the form with a signature.
While Form W-9 is a short form, make sure to avoid common errors by following our step-by-step instructions on how to fill out Form W-9.
W-9 vs. Form 1099 overview
Form W-9 and Form 1099 are both used for tax reporting in the US, but each form serves a different purpose.
Form W-9 is used for the submission of a TIN and other important information, while Form 1099 is used to report non-employment income — specifically when the income is $600 or more for that year.
Another difference between these forms is who is required to fill them out. A payee will submit Form W-9 at the request of a payer, and a payer will file Form 1099 to the IRS, using the payee’s information submitted in the W-9, to report the payee’s non-employment income.
For a detailed comparison, read more about the difference between Form W-9 and 1099.
Reporting and withholding
Backup withholding is an important factor regarding Form W-9. For payees who fail to submit Form W-9 or provide a correct TIN, a 24% withholding rate will be paid to the IRS, deducted from the payee’s income.
Backup withholding ensures that non-employment income is reported to the IRS. Payees must submit Form W-9 to certify that they are not subject to backup withholding, and payers must file Form 1099 to report non-employment income to the IRS.
If a payee fails to submit Form W-9 or provide a correct TIN, it becomes the payer’s responsibility to resort to backup withholding and remit to the IRS the 24% withholding rate.
In some cases, payees and payments can be exempt from backup withholding.
FAQs
What is the most current W-9 form and where can I find it?
The most up-to-date W-9 form can be found on the IRS website as a PDF file. It can be printed and filled out by hand, or downloaded and filled out electronically.
How does a W-9 form work and when is it needed?
Form W-9 is needed for the submission of a TIN. This can be for owed income, real estate transactions, mortgage interest, acquisition or abandonment of secured property, cancellation of debt, or contributions made to an IRA.
What is a W-9 form used for, and why is it important for tax reporting?
Form W-9 is used for tax purposes. It provides businesses or companies with a payee’s TIN and other information, so that the business or company can report a payee’s non-employment income to the IRS through Form 1099.
How do businesses and freelancers use the W-9 form?
Form W-9 is commonly used by businesses and freelancers. A business will request Form W-9 from a freelancer to receive their TIN. With this information, a business must file Form 1099 to report non-employment income of $600 or more to the IRS.
What are the legal responsibilities associated with filling out a W-9?
Both payers and payees have legal responsibilities regarding Form W-9. After requesting Form W-9 from a payee, a payer must report non-employment income of $600 or more to the IRS through Form 1099. A payee must submit Form W-9 when it is requested to avoid backup withholding and other penalties.
Are there any privacy concerns I should be aware of when providing information on a W-9?
W-9 forms are protected by the Internal Revenue Code (IRS), the Privacy Act of 1974, and the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act, which prohibit the disclosure of taxpayers’ private information. To further protect your information, always make sure to securely submit Form W-9 to the requester.
What should I do if my information changes after submitting a W-9 form?
If you need to make changes to the information you have submitted on Form W-9, it’s best to inform the requester and provide a new W-9 form with the correct information. You can also accompany the new form with a letter highlighting any changes you have made.
How do I report income from a W-9 and understand withholding requirements?
Form W-9 is used to submit a TIN and other information to a requester, who can then report necessary payments through Form 1099. It’s important to submit Form W-9 when it is requested to certify that you are not subject to the 24% withholding rate on non-employment income.
What does the term ‘taxpayer identification number (TIN)’ mean in the context of a W-9?
The Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) on Form W-9 is a Social Security number (SNN) for individuals or an Employer Identification Number (EIN) for other entities. It’s important to provide the correct TIN on Form W-9 to avoid penalties and backup withholding.
Are there any specific considerations for non-U.S. citizens regarding Form W-9?
Form W-9 does not apply to non-US citizens; it only applies to US citizens and US resident aliens (i.e. foreign-born US residents who are not US citizens). Non-US citizens who will receive income from a US-based business must submit Form W-8 instead, which is used to declare foreign status.
Can a W-9 form be filed electronically, and what are the benefits?
Form W-9 can be filed electronically provided that the requester has an established system that allows for accurate electronic filing. The W-9 form must be submitted with the same information on the paper Form W-9 and a valid electronic signature.
Conclusion
To wrap up, Form W-9 is a simple form that’s used for the submission of a TIN to a requester.
This is common between businesses and independent contractors — a business will request Form W-9 from an independent contractor and, once received, report the independent contractor’s non-employment income to the IRS by filing Form 1099. This is a requirement if the non-employment income is $600 or more for that year.
As failure to submit Form W-9 can result in penalties for both payers and payees, it’s important that the form is submitted correctly. If you need further assistance, you can always reach out to a tax professional for personalized advice.

Thank you! The eBook has been sent to your email. Enjoy your copy.
There was an error processing your request. Please try again later.
Looking to boost your firm's profitability and efficiency?
Download our eBook to get the answers



